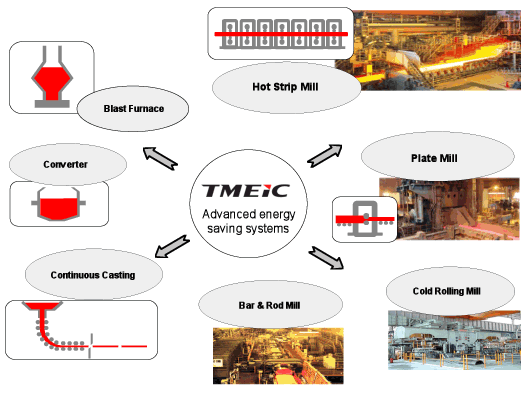
The steel industry is energy intensive with many opportunities to apply advanced controls to save energy. Some of the possible energy saving applications in a steel mill and the potential annual savings are illustrated in the figure below.
Energy saving systems typically use variable frequency drives, mill feedback data, and expert mill operation knowledge to precisely control and reduce the energy flows through the equipment. Some of the actual savings achieved by TMEIC on hot strip mills are shown below.
- Main Motor Cooling Fan – Energy savings through speed control of the cooling fan based on the load on the motor, winding temperature, and air temperature.
- Auxiliary Motor Cooling – Energy savings through speed control of the cooling fan based on the load on the motor, winding temperature, and air temperature.
- Fume Exhaust Fan – Energy savings through fan speed control based on the exhaust air flow.
- Cooling Water Pump – Energy savings through pump speed control based on the tank level and calculated flow of cooling water to the run out table.
- Scale Pit Pump – Energy savings through pump speed control based on position of the slab relative to the descaler.
The following table shows the energy saving technology for each facility in a steel plant.
|
Plan |
Equipment |
Mechanical equipment and system technology |
|---|---|---|
|
Manufacture of Pig Iron |
Combustion equipment |
|
|
Collection of waste heat |
|
|
|
Other Processes |
|
|
|
Steel Making |
Waste Heat Recovery |
|
|
Sintering Plant |
|
|
|
Collection of waste heat |
Material preheating equipment for electric furnace |
|
|
Electrical Energy Saving |
|
|
|
Rolling/ Surface Treatment |
Collection of waste heat |
|
|
Electrical Energy Saving |
|
|
|
Rod/ Shaping/ Fabrication |
Heat utilization equipment |
Speed control of furnace blower |
|
Collection of waste heat |
|
|
|
Electrical Energy Saving |
|
|
|
Other Energy Consumption Plant |
Cogeneration equipment |
|
|
Electric power use equipment |
|
|
|
Lighting system |
|
Abstract from "Type 1 specified Business Operator" the guide for mid and long term scenario- (4) Steel Plant publication in Japan by ECCJ, Japan 1999 with TMEIC's amendments from electrical point of view.
TMEIC introduces the following electrical energy saving technologies for metal mills:
Energy Saving System for Rolling Mills and Process Lines
Features
- Providing optimal energy savings for complete rolling mills and process lines
- Providing an energy saving system which can be easily added to an existing mill
- Using a combination of PLC controllers and drives
Applications
- Energy saving using variable speed drive control
- Optimal cooling of drive motor
- Energy savings for miscellaneous power, lighting, and heaters (example: Stop while idling)
- Optimal operation using energy saving control model (example: heating furnace combustion control and mill pacing)
- Waste heat recovery
Energy Saving Controls for Hot Strip Mills
Furnace combustion control
- Improved fuel consumption using furnace combustion control model
- Reduction of material heat emission using mill control model
Improvement of power factor
- Improving efficiency and power factor by applying GCT/IEGT main drives
- Monitoring power demand for the entire mill line
- Reduction of electric power rates by improving power factor
Optimization of Ventilation cooling
- Optimal control using variable speed control
- Main motor cooling fan
- Auxiliary motor cooling fan
- Electrical room ventilation cooling fan
Applying Variable Voltage, Variable Frequency Control
- Descaler pump
- Air compressor
- Heating furnace blower
- Conveyor system
Energy saving operation
- Energy saving control of miscellaneous power, lighting and air conditioning units
Introduction of energy saving equipment
- Applying high efficiency motors
- Applying high efficiency transformers
- Replacing DC motors with AC motors and variable speed drives
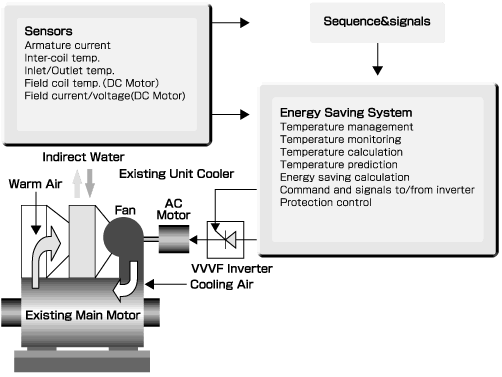
Energy Saving Control System for Hot Strip Mill Main Motor Cooling Fan
In order to remove the heat generated in the main motor rotor and stator, cooling air is circulated through the unit cooler. The speed of the cooling fan motor is varied proportionally to the load of the main motor, thereby providing energy conservation.
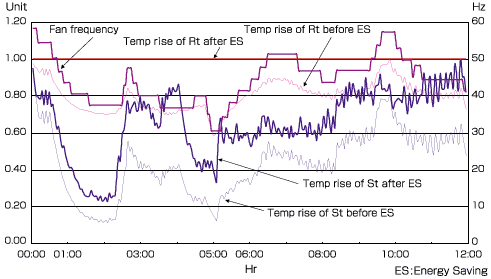
Typical plot of Fan Frequency and Motor Temperature
This graph shows an example of controlling the main motor cooling fan speed so the temperature rise of the motor remains constant irrespective of the main motor load. By applying this technology, large energy savings have been realized as shown in the following table.
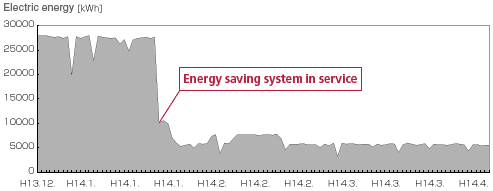
This graph shows the power reduction by applying TMEIC's energy saving control system in a steel company.